Brake Pad Visual Inspection with AI Computer Vision
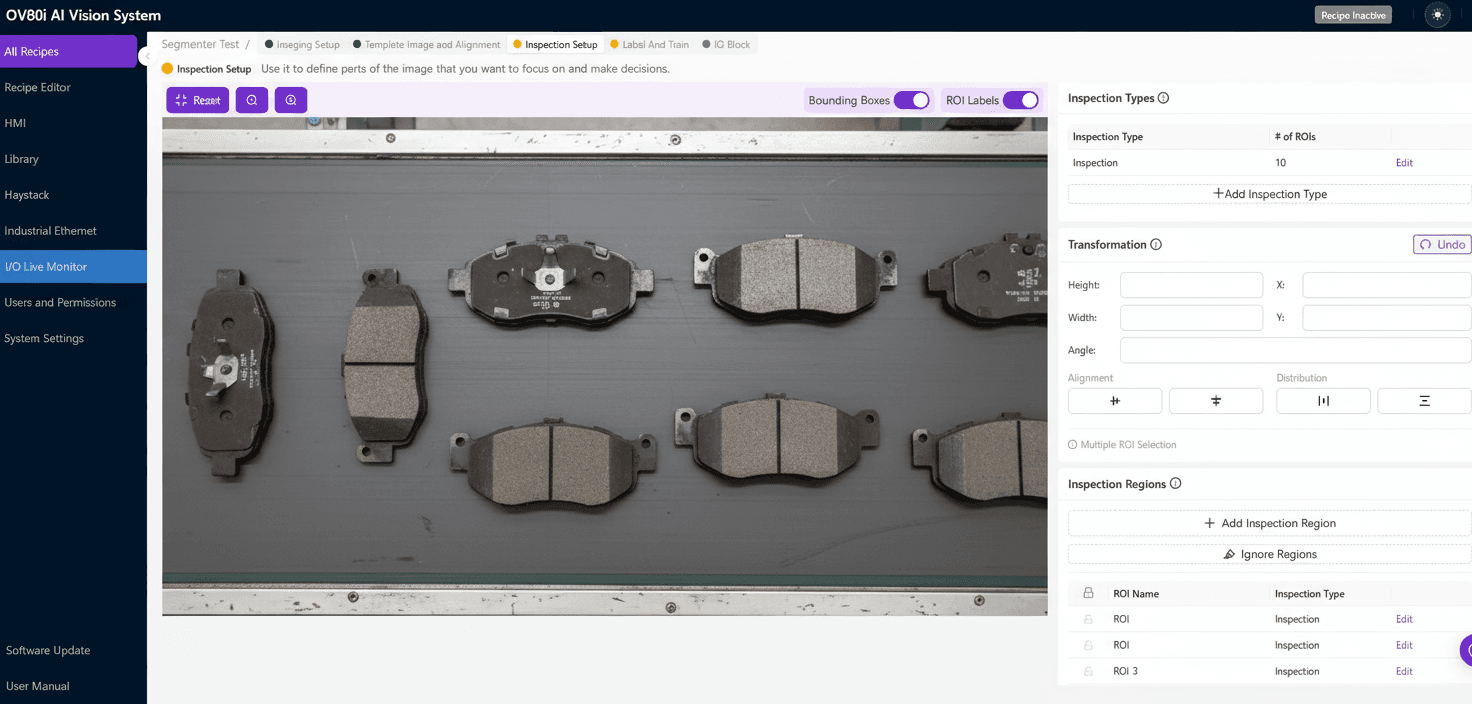
Brake pad quality is safety-critical, yet manual checks miss micro-defects, dimensional drift, and assembly errors at line speeds. AI-powered machine vision systems deliver 100% inline inspection, metrology, and assembly verification—reducing escapes, rework, and NVH-related returns while improving throughput and traceability.
The Problem: Why Traditional Brake Pad QC Misses Defects That Matter
Visual inspection of brake pads sounds straightforward—until you scale to high-mix SKUs, dark friction materials, dusty environments, and sub-millimeter tolerances. Human inspection and go/no-go gauges struggle with consistency and coverage, especially under takt-time pressure.
What goes wrong in practice:
- Micro-defects are inherently hard to see
Hairline cracks, chips, voids, and porosity on black friction surfaces; Adhesive squeeze-out or thin bond lines that predict delamination; Incomplete paint or powder coat coverage on backing plates. - Dimensional drift is gradual and multi-factor
Thickness variation, taper, wedge, and flatness after grinding; Chamfer angle, length, and slot width/position variations driving NVH; Sensor rivet height and shim compression out of spec. - Assembly errors escape intermittently
Missing/misaligned shims, springs, clips, or wear indicators; Wrong pad/shim combination (mix-up) due to SKU proliferation; Cable routing errors on wear sensors and incorrect orientation. - Surface and material conditions hide defects
Scorching uniformity hard to judge by eye; over/under-burn affects bedding; Oil/grease contamination and embedded debris; Glare from coatings, texture variation after shot-blast. - Process realities outpace humans and hand tools
Line speeds that limit dwell time to a fraction of a second; Fatigue and subjectivity between shifts and sites; Spot checks and calipers measure only a few points, not the whole pad. - The cost of escapes is high
NVH complaints (squeal, vibration), premature wear, and warranty claims; Safety and brand risk in a regulated, IATF 16949 environment; Rework loops that slow flow and hide upstream process issues.
Traditional QC is not designed for 100% coverage of complex surfaces and assemblies in real time. That’s where automated visual inspection with AI becomes decisive.
The Solution: AI Vision for 100% Inline Brake Pad Inspection
AI computer vision transforms brake pad quality from sample-based checks to continuous, comprehensive inspection. A modern vision inspection system combines tailored lighting, multi-view cameras, 2D/3D metrology, and deep learning to detect subtle appearance defects and verify assembly at production speed.
How a production-ready system is built:
- Robust imaging at speed: Multi-camera views, structured light for 3D, and specialized lighting to expose defects.
- AI models tuned for brake pads: Defect segmentation, keypoint models, classification, and OCR for traceability.
- Metrology-grade performance: Sub-0.1 mm repeatability, automatic compensation for drift, and SPC dashboards.
- Industrial integration: PLC handshakes, dust-resistant enclosures, recipe control for high-mix lines, and centralized management.
What AI vision detects on brake pads:
- Friction material: Thickness, flatness, chamfers, slots, cracks, voids, scorching uniformity, and contamination.
- Backing plate and bonding: Plate geometry, burrs, adhesive coverage, squeeze-out, and paint quality.
- Assembly verification: Presence and alignment of shims, clips, springs, and wear indicators; sensor rivet height and cable routing.
- Mix-up prevention and traceability: Real-time SKU recognition and barcode/OCR checking against order data.
By closing the loop between detection and data, machine vision systems don’t just reject bad parts; they expose upstream causes so you can fix processes—grinding drift, chamfer tool wear, adhesive dispense variability, or scorching oven imbalance.
Key Applications & Outcomes
Where to inspect on a typical pad line:
- Post-press/sinter: Detect cracks, delamination risk, porosity.
- Post-grinding/chamfer/slotting: Measure critical dimensions, flag chips and burrs.
- Post-scorch/paint: Verify burn pattern and coating coverage.
- Assembly cell: Full assembly verification (shims, clips, sensors).
- Final pack and labeling: Count, label legibility, and SKU/order match.
Business outcomes you can quantify:
- Fewer escapes, fewer returns: Move from ppm to near-zero escapes and cut NVH complaints.
- Less rework and higher yield: Early detection prevents adding value to scrap and enables data-driven maintenance.
- Higher throughput and labor efficiency: Inline decisions in under 200ms allow redeployment of manual inspectors.
- Compliance and traceability: End-to-end serialization and digital records for audits.
- Continuous process improvement: Trend analysis helps target and fix root causes upstream.
Why now:
- AI models now outperform hand-coded rules on low-contrast brake pad surfaces.
- Off-the-shelf cameras and lighting meet metrology needs at lower cost.
- No-code/low-code deployment accelerates time-to-value, even on high-mix lines.
If you’re still relying on manual checks and occasional gauges, you’re accepting variability you don’t need. A modern vision inspection system with AI computer vision delivers consistent, objective results at line speed, elevating brake pad quality from inspection to assurance.
Looking to implement brake pad visual inspection or upgrade legacy systems? Overview’s machine vision systems combine AI accuracy with production-grade reliability, helping brake manufacturers scale zero-defect quality with real-time, actionable data.
See It in Action
Explore the OV80i and ask us about advanced inspection packages for your specific application.