Opening the Black Box: How Haystack Brings Transparency to Industrial AI
In the world of manufacturing, a "black box" is a liability. When an automated vision system flags a part as a "Fail," quality engineers need to know why. Without that insight, debugging a model becomes a process of trial and error that wastes time and resources.
At Overview, we believe AI should be as transparent as any other tool on your factory floor. That’s why we built Haystack—a visualization framework that turns complex AI logic into an intuitive, interactive 2D map.
What is Haystack?
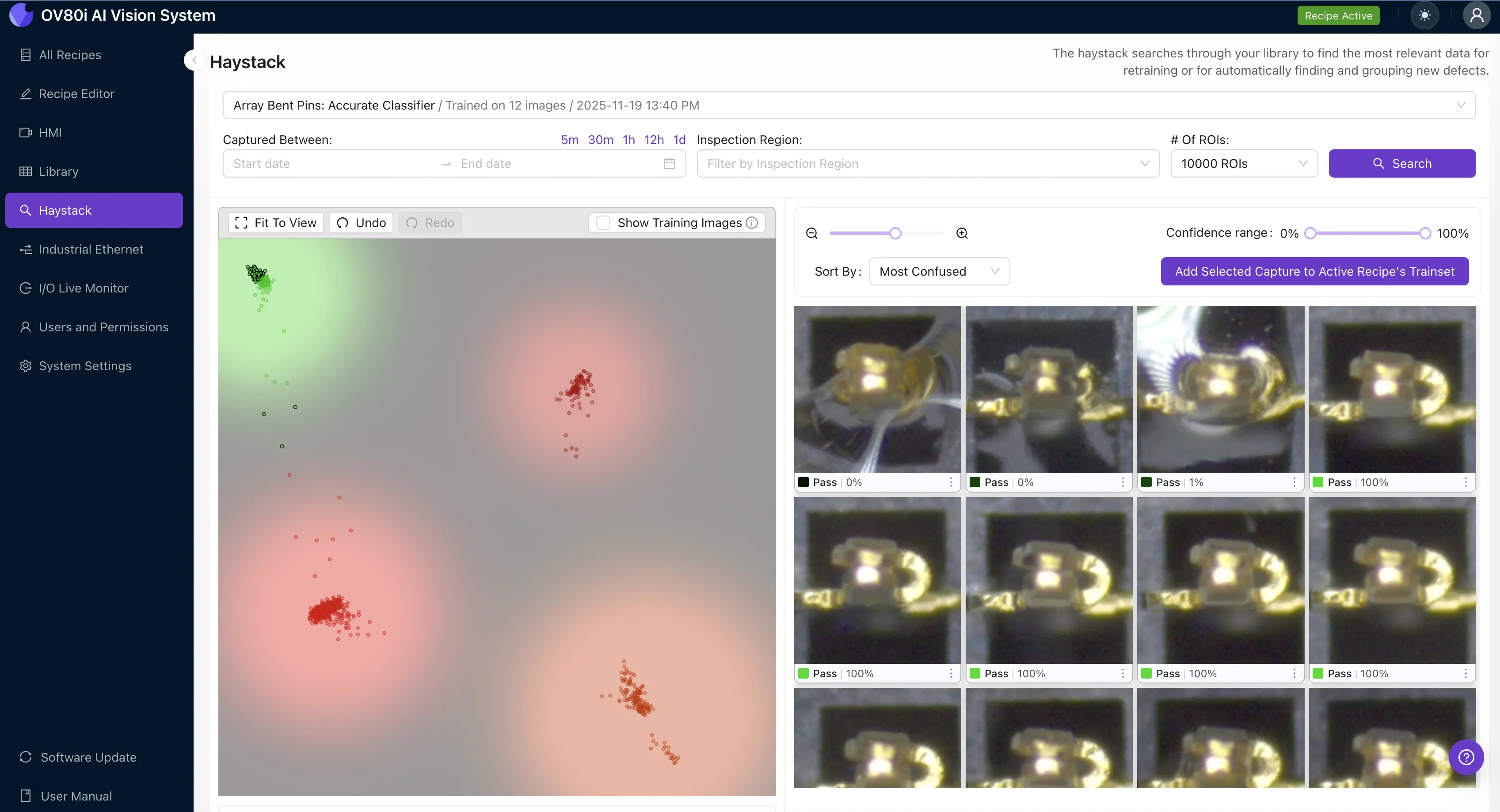
Deep learning models "see" images as high-dimensional math, which is impossible for a human to interpret. Haystack acts like a translator. It takes those complex data points and projects them onto a 2D "Haystack space" where similar images cluster together.
Think of it as Google Maps for your inspection data. Instead of looking at thousands of individual photos, you see a landscape of your production quality. "Good" parts cluster in one neighborhood, while different types of defects—like scratches, dents, or missing components—form their own distinct "towns" on the map.
Analogy for the Factory Floor
Imagine your factory's data is a giant, unorganized pile of thousands of polaroid photos. Finding a specific defect is like looking for a needle in a haystack.
Haystack is like a high-speed sorting machine that instantly organizes those photos into neat piles based on what they show. It then lays those piles out on a giant table so you can see at a glance where the "Pass" pile ends and the "Fail" pile begins—and exactly which photos are sitting on the line in between.
Stop Guessing, Start Debugging
For a quality engineer, Haystack is a powerful diagnostic tool. By looking at the map, you can immediately identify:
- Confusion Regions: Areas where "Pass" and "Fail" images overlap. This tells you exactly where the model is uncertain.
- Outliers: A single "Pass" dot sitting in the middle of a "Fail" cluster often reveals a mislabeled image or a subtle new defect type.
- Robustness: You can see how the model handles variations like lighting changes or reflections, ensuring it remains stable in real-world conditions.
The "Lasso" Tool: Training AI in Seconds
One of the most innovative features of Haystack is the interactive lasso tool. Traditionally, retraining a model meant manually sorting through thousands of images to find the ones the AI struggled with.
With Haystack, you can simply draw a circle around a cluster of uncertain images on the map and add them to a training set with one click. This "active learning" workflow allows engineers to move from detection to action instantly, closing the loop on continuous improvement.
Proven Performance with Minimal Data
Because Haystack is integrated into Overview’s high-performance backbone, it doesn't need much data to be effective:
- Speed: You can train a functional recipe in under a minute.
- Efficiency: Some of our most complex applications—like inspecting high-voltage wire braids or soft-seated connectors—achieved 100% accuracy with as few as 10 to 20 images.
- Tough Environments: When paired with our OV20i hardware, Haystack uses "photometric mode" to strip away glare from shiny surfaces, making even the smallest scratches visible on the map.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How many images are required to train a model and generate a functional Haystack map?
Unlike traditional vision systems that require thousands of samples, Overview’s deep learning architectures are optimized for small datasets, often requiring as few as 4 to 20 images to achieve high accuracy. The Fast Classifier option allows for the rapid generation of a Haystack map and decision boundaries in as little as 45 seconds, enabling engineers to validate a new recipe almost instantly. This efficiency is driven by task-aware projection heads that maximize class separability even with minimal data.
How does Haystack handle highly reflective surfaces or inconsistent factory lighting?
Haystack is part of a hardware-software ecosystem designed specifically for "formidable" environments, such as those involving shiny or reflective objects. The system utilizes a photometric mode on the OV20i hardware to eliminate glare and reveal subtle defects like scratches or pits that are otherwise invisible. Because the underlying RBF-based classification is robust to variation, the resulting Haystack map remains stable despite changes in ambient lighting or operator handling, ensuring that decision boundaries do not shift erratically in real-world production conditions.
Can Haystack be integrated into existing factory workflows and control systems?
Yes, Haystack is designed to be actionable, not just diagnostic. The system integrates seamlessly with factory ecosystems through a no-code workflow builder that can trigger real-time actions—such as signaling a PLC to stop a line, updating an MES, or sending a Slack alert—the moment a defect is detected. Furthermore, the interface includes an active-learning lasso tool, allowing quality engineers to select uncertain samples directly from the 2D visualization and immediately queue them for retraining to close the loop on continuous process improvement.
Want to see your data on the map?
Schedule a demo with an Overview engineer today to see how Haystack can transform your quality control process.
Schedule a Demo